JS Task API Examples: executing tasks
Introduction
With Golem JS Task API you can execute just a single task on a single provider or a series of multiple tasks in parallel on many providers. In the case of the latter, you can additionally define how providers should be initialized and how many tasks you want to run simultaneously.
In this article, the following examples are presented:
- Running tasks in parallel (map())
- Running tasks in parallel (forEach())
- Defining the number of providers working in parallel
- Initializing providers
- Running a single task
Prerequisites
Yagna service is installed and running with the try_golem app-key configured.
This example has been designed to work with the following environments:
- OS X 10.14+, Ubuntu 20.04 or Windows
- Node.js 16.0.0 or above
How to run examples
Create a project folder, initialize a Node.js project, and install the @golem-sdk/golem-js library.
mkdir golem-example
cd golem-example
npm init
npm install @golem-sdk/golem-jsCopy the code into the index.mjs file in the project folder and run:
node index.mjsRunning tasks in parallel using the map() method
If you want to run your tasks in parallel, you can use the map() method.
import { TaskExecutor } from "@golem-sdk/golem-js";
(async () => {
const executor = await TaskExecutor.create({
package: "529f7fdaf1cf46ce3126eb6bbcd3b213c314fe8fe884914f5d1106d4",
yagnaOptions: { apiKey: "try_golem" },
});
const data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const futureResults = data.map(async (item) =>
executor.run(async (ctx) => {
return await ctx.run(`echo "${item}"`);
}),
);
const results = await Promise.all(futureResults);
results.forEach((result) => console.log(result.stdout));
await executor.end();
})();
The method map() accepts an array that defines the total number of tasks to be executed and may contain the data used to define a task. In the example, we have an array of 5 elements [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] and we use these values within the task function to define task steps. For each task, another element from the data array is passed as an item and then used to customize the argument for the echo command.
Note that the result of the executor map() is an asynchronous iterable object with each element accessible with the for await statement.
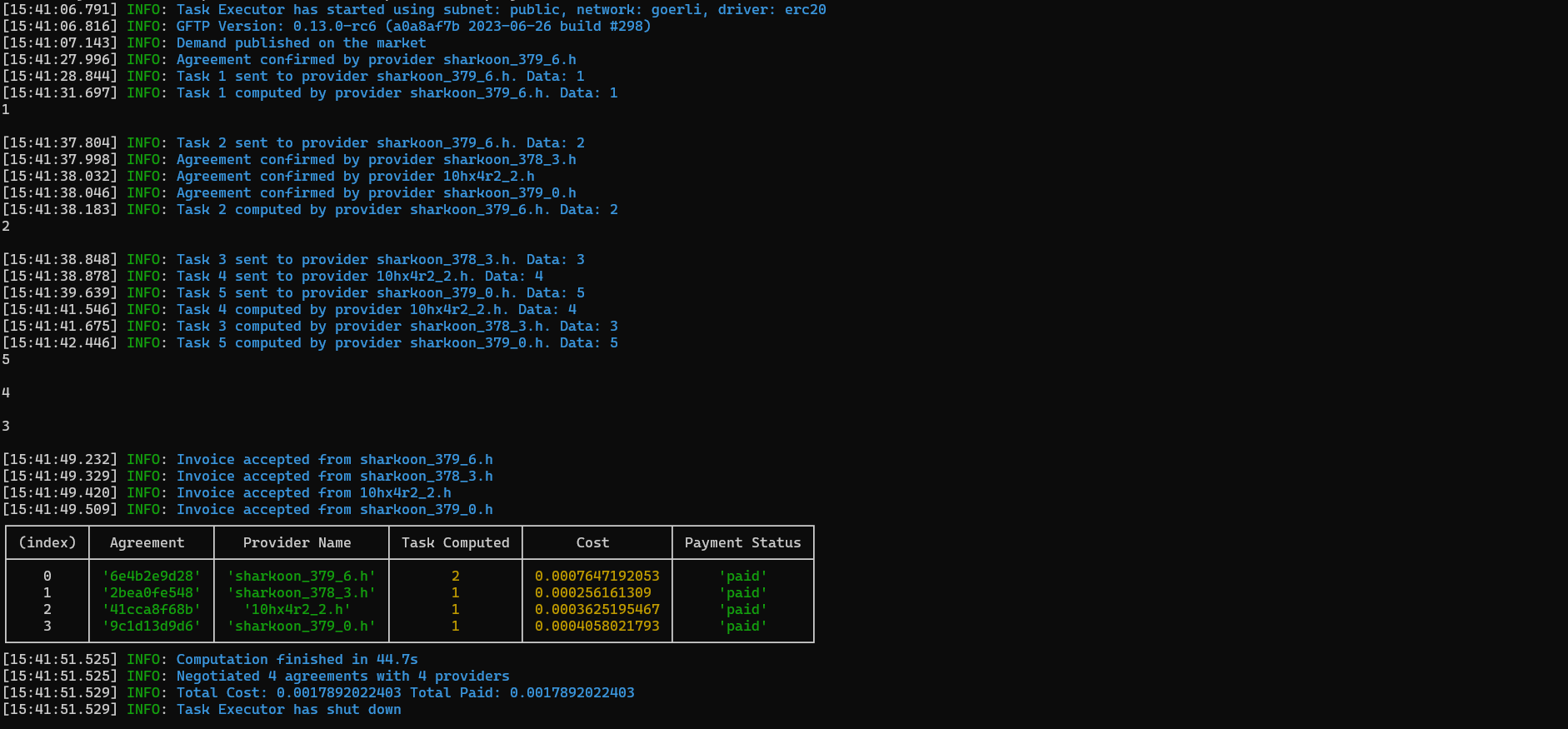
In the output logs, you can have some interesting observations:
The provider sharkoon_379_6 was engaged first. When he had finished his first task he was still the only available provider and he received another task to execute. In the meantime, other providers were successfully engaged and the next tasks were dispatched to them.
Note that even though provider sharkoon_379_8 was engaged before provider 10hx4r2_2.h, the latter completed its task before the former. In the network, different nodes offer varying performance.
Running multiple tasks in parallel using the forEach() method
If you do not need an object to facilitate the processing results of all the tasks, you can use another method that can also execute tasks in parallel. Even if the forEach() method does not return an object to iterate through, you can still access the result object for each command within the task function.
import { TaskExecutor } from "@golem-sdk/golem-js";
(async () => {
const executor = await TaskExecutor.create({
package: "529f7fdaf1cf46ce3126eb6bbcd3b213c314fe8fe884914f5d1106d4",
yagnaOptions: { apiKey: "try_golem" },
});
const data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
for (const item of data) {
await executor.run(async (ctx) => {
console.log((await ctx.run(`echo "${item}"`)).stdout);
});
}
await executor.end();
})();
Defining the number of providers used
You can set the maximum number of providers to be engaged at the same time. The TaskExecutor will scan available proposals and engage additional providers if the number of actually engaged providers is lower than maxParallelTasks and there are still some tasks to be executed. If you do not define this parameter, a default value of 5 will be used.
Note that the actual number of engaged providers might be:
- lower than
maxParallelTasks, if there are not enough providers available in the network. - higher, when considering the total number of engaged providers for all the tasks in your job. Providers might get disconnected or simply fail, in which case the TaskExecutor will engage another one to maintain the number of active workers at the level defined by
maxParallelTasks.
Below, you can see how to define the maximum number of providers to be engaged.
import { TaskExecutor } from "@golem-sdk/golem-js";
(async () => {
const executor = await TaskExecutor.create({
package: "529f7fdaf1cf46ce3126eb6bbcd3b213c314fe8fe884914f5d1106d4",
yagnaOptions: { apiKey: "try_golem" },
maxParallelTasks: 3, // default is 5
});
const data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const futureResults = data.map(async (item) =>
executor.run(async (ctx) => {
return await ctx.run(`echo "${item}"`);
}),
);
const results = await Promise.all(futureResults);
results.forEach((result) => console.log(result.stdout));
await executor.end();
})();
Initialization tasks
Normally, when a larger job is divided into smaller tasks to be run in parallel on a limited number of providers, these providers might be utilized for more than one task. In such cases, each task is executed in the same environment as the previous task run on that provider. To optimize performance, you might decide that some initialization tasks need only be run once per provider. This can be particularly useful if you have to send a large amount of data to the provider.
This example requires an action_log.txt file that can be created with the following command:
echo Action log: > action_log.txtYou can address such a need using the beforeEach() method of the TaskExecutor. Here is an example:
import { TaskExecutor } from "@golem-sdk/golem-js";
(async () => {
const executor = await TaskExecutor.create({
package: "529f7fdaf1cf46ce3126eb6bbcd3b213c314fe8fe884914f5d1106d4",
yagnaOptions: { apiKey: "try_golem" },
maxParallelTasks: 3,
});
executor.beforeEach(async (ctx) => {
console.log(ctx.provider.name + " is downloading action_log file");
await ctx.uploadFile("./action_log.txt", "/golem/input/action_log.txt");
});
const inputs = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const futureResults = inputs.map(async (item) => {
return await executor.run(async (ctx) => {
await ctx
.beginBatch()
.run(`echo ` + `'processing item: ` + item + `' >> /golem/input/action_log.txt`)
.downloadFile("/golem/input/action_log.txt", "./output_" + ctx.provider.name + ".txt")
.end();
});
});
await Promise.all(futureResults);
await executor.end();
})();
In the code, we decreased the maxParallelTasks value from the default value of 5, to make sure that some of our five tasks will be run on the same provider.
The beforeEach() method is used to upload a file to a remote computer that will be used to log all future activity run on this provider. The task function used in the beforeEach() method contains an additional console.log to demonstrate that even if the whole job consists of five tasks, the task function used in beforeEach() will be executed only once per provider. (Unless the provider disengages and is engaged again - in such a situation, its virtual machine would be created anew, and we would upload the file again there).
Note how we utilized the ctx worker context to get the provider name using the provider.name property.
In the task function used in the forEach() method, we employed the beginBatch() to chain multiple commands - you can see more about this feature in the Defining Tasks article.
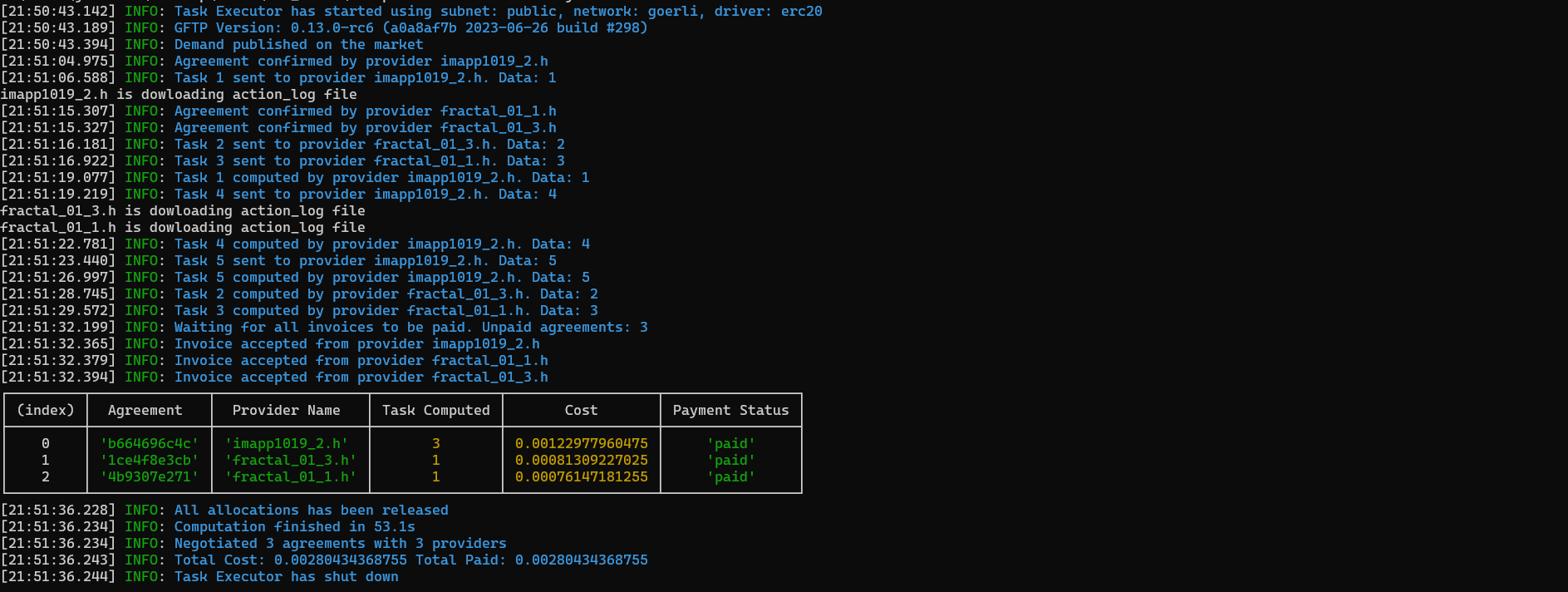
The log from this example shows that even if the provider imapp1019_2.h was eventually used to execute 3 tasks, it uploaded the log only once. Its output file - downloaded after the last task was executed - contained the following:
---------------------------
processing item: 1
processing item: 4
processing item: 5This log once again illustrates that providers offer different performance levels. Even though fractal_01_1.h and fractal_01_3.h signed agreements before Task 1 was computed on imapp1019_2.h, this provider managed to complete Tasks 4 and Task 5 before they downloaded the action_log file and completed their first task.
Single run
Sometimes you don't need to run tasks in parallel and a single run is sufficient. In such cases, you can use the run() method as demonstrated in the example below.
import { TaskExecutor } from "@golem-sdk/golem-js";
(async () => {
const executor = await TaskExecutor.create({
package: "529f7fdaf1cf46ce3126eb6bbcd3b213c314fe8fe884914f5d1106d4",
yagnaOptions: { apiKey: "try_golem" },
});
const result = await executor.run(async (ctx) => (await ctx.run("node -v")).stdout);
await executor.end();
console.log("Task result:", result);
})();
The requestor script runs a single task defined by a task function: ctx.run("node -v"). The output of the command is available through stdout of the result object returned from the ctx.run() function:
Below, you can see the script logs:
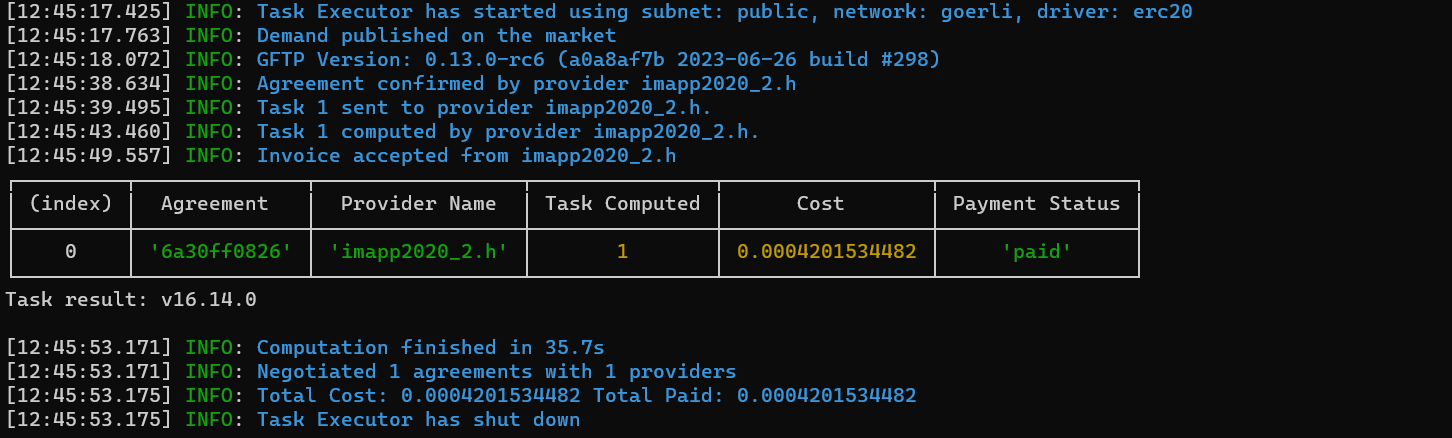
In the logs, we can see that the requestor uses the Goerli network for payments (a test network). The task was executed once on a single provider.
In the table, we see a summary of the costs (paid here in test GLM), along with the result of the command which outputs the version of the node in the image deployed on the provider.